Small Left Colon Syndrome
Small left colon syndrome. In this situation it is also termed the small left colon syndrome. Small left colon syndrome refers to a dysfunctional diminutive left colon that causes transient obstructive symptoms. It is generally regarded as a functional immaturity of the colon resulting in failure to pass the first stool.
MATERIAL AND METHOD Nineteen infants presented inthe first to third days oflife each ofwhom had essen-tially the same clinical history suggesting low colonic obstruction. NSLCS has a favourable prognosis but needs close follow-up in view of late complications. Early suspicion of this diagnosis averts unnecessary invasive interventions and surgery.
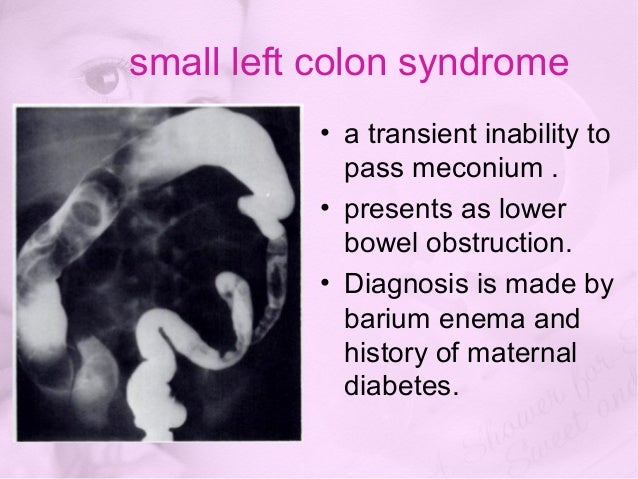
Occurrence in asymptomatic infants of diabetic mothers. Its etiology remains unknown but a significant association has been noted between maternal diabetes and small left colon. The diagnosis and treatment are assured by a simple contrast enema.
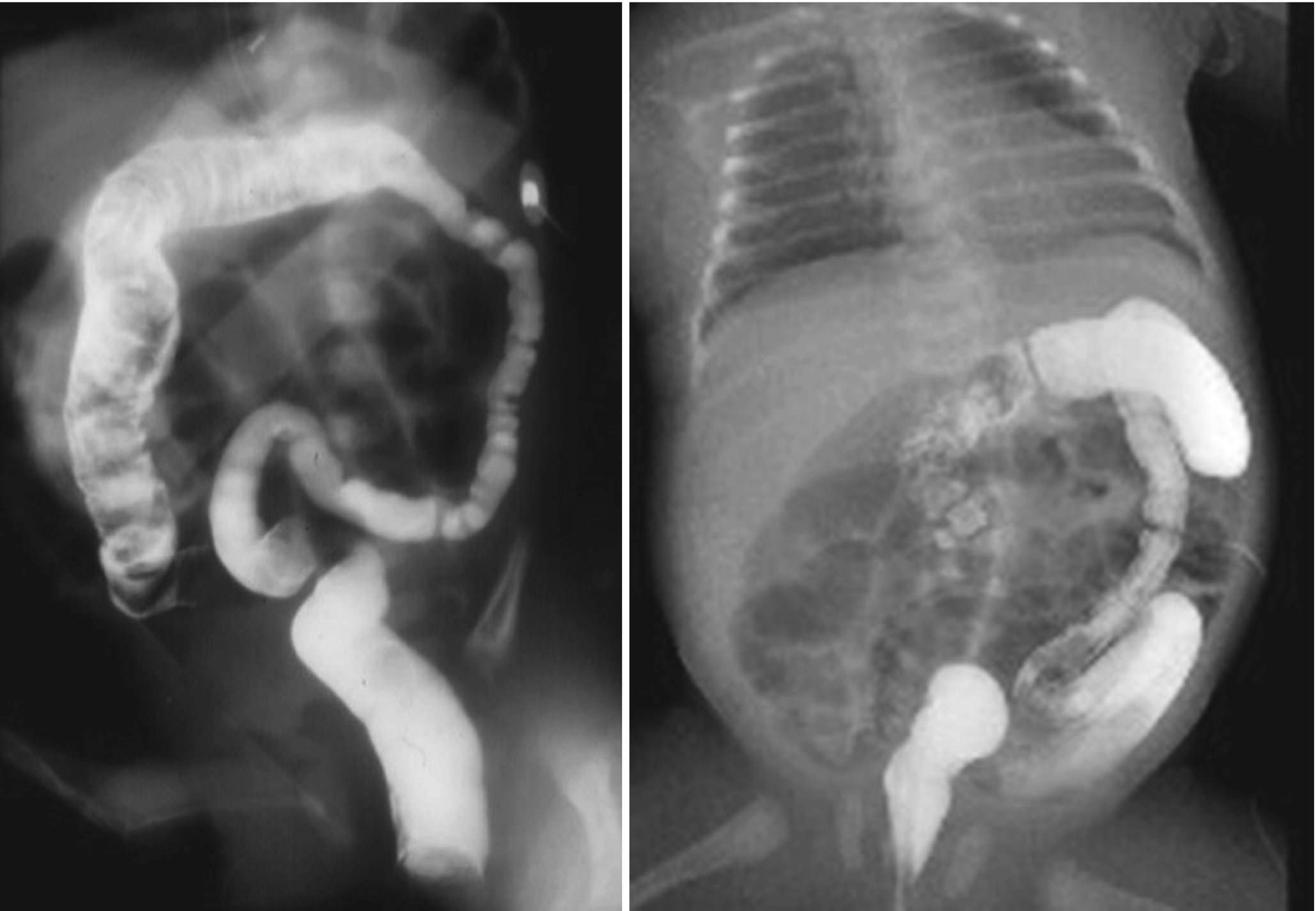
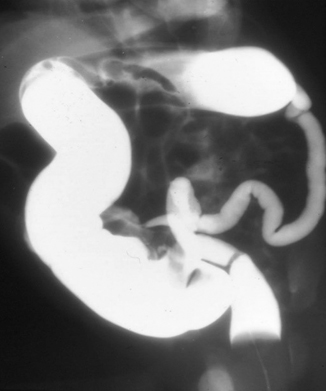
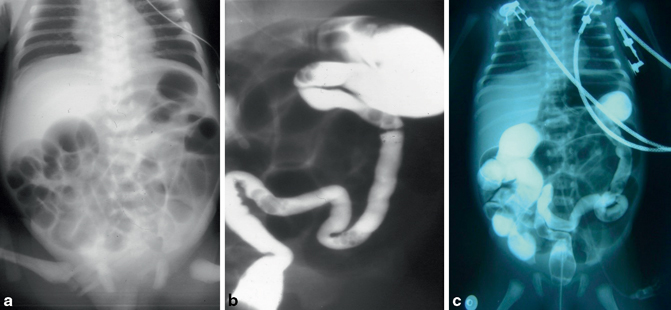
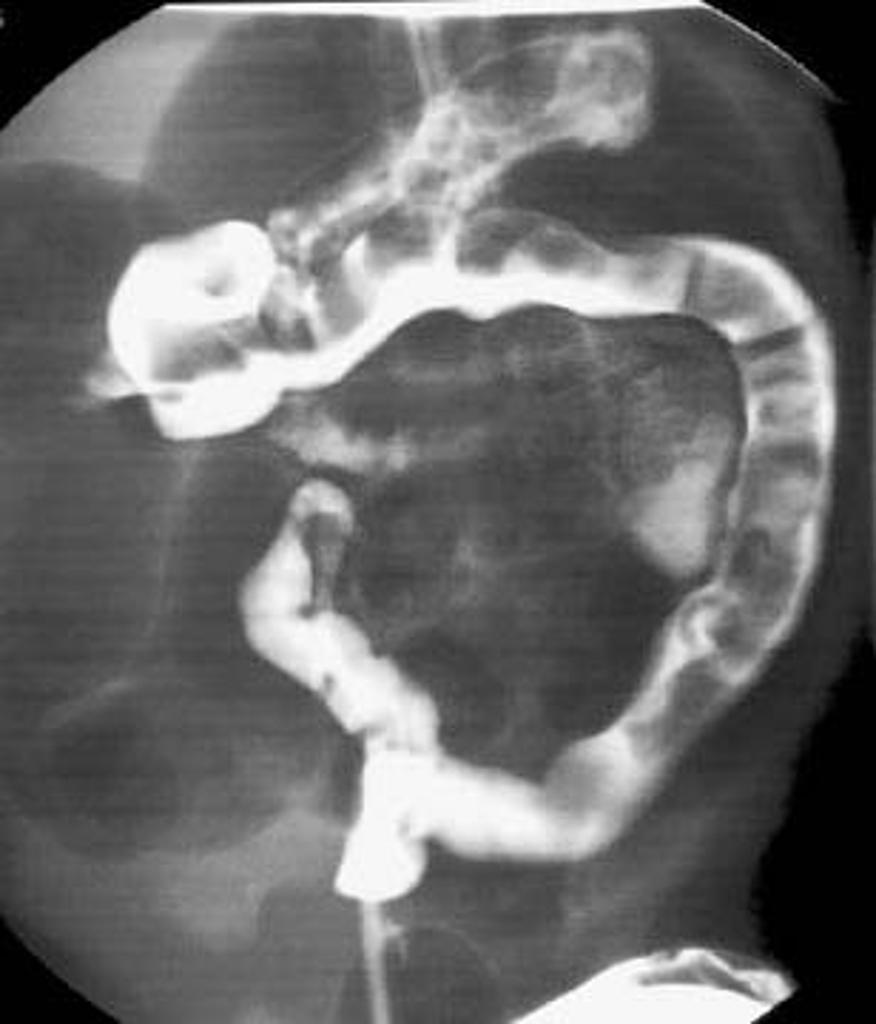
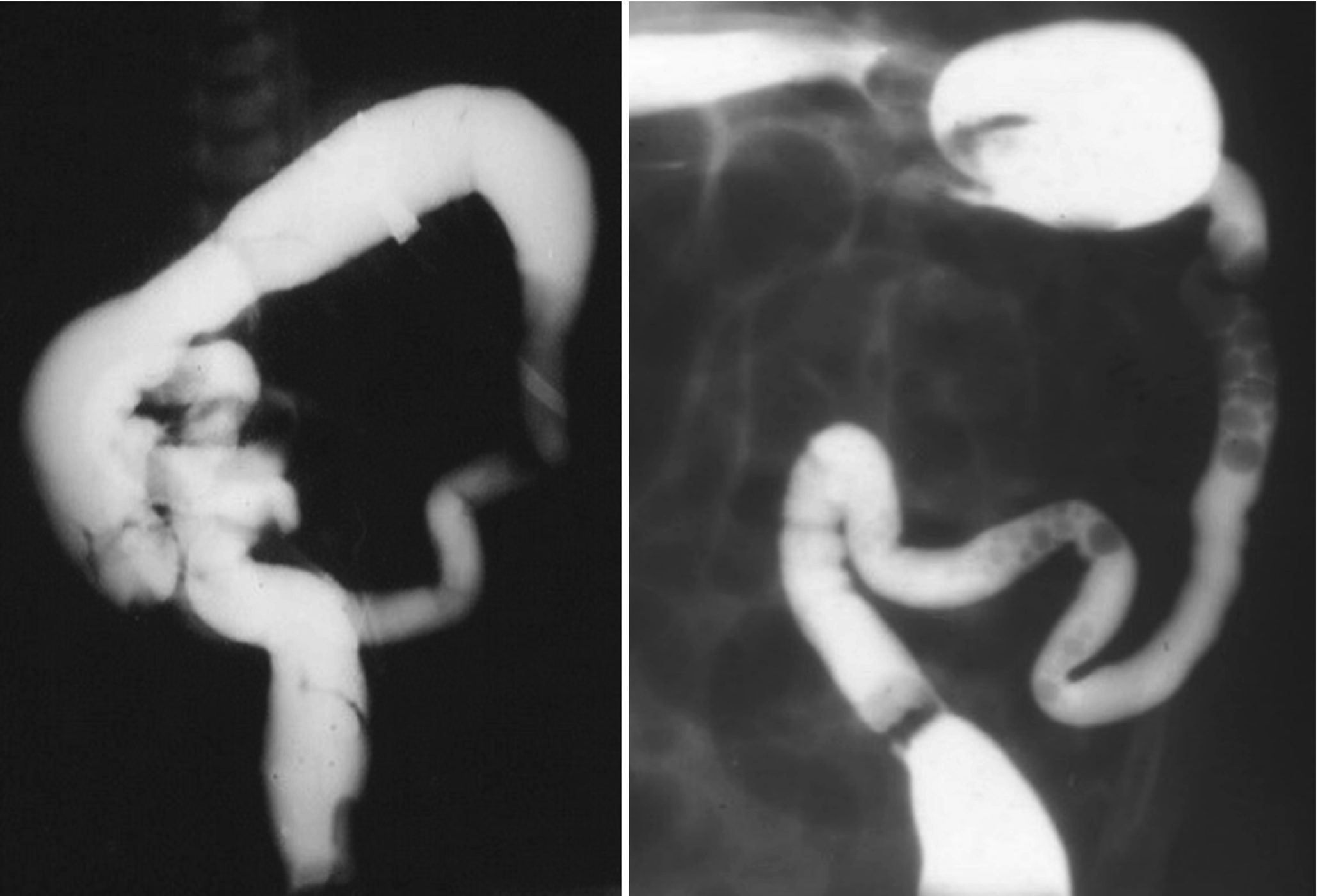
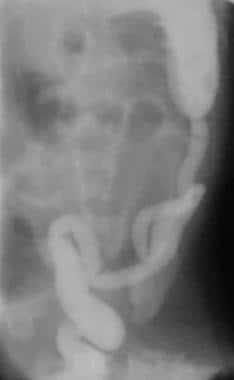
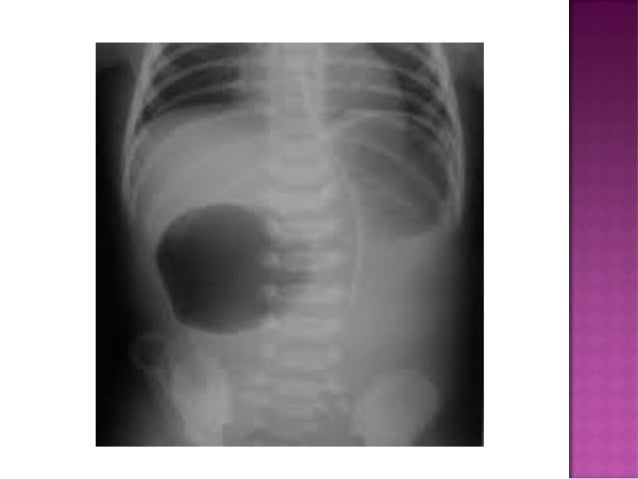
Small left colon sydrome is subset of meconium plug syndrome in which an enema demonstrates an apparent transition zone between the dilated and the normal-to. Plain abdominal radiographs show dilated intestinal loops. Affected patients have abdominal distention difficulty in initiating evacuation and sometimes vomiting.
An unusually high incidence 40 of maternal diabetes was observed in a series of 20 newborn infants who had low colonic obstruction and barium enema findings of a uniformly narrowed colon from the splenic flexure to the anus. Hyperglucagonemiawhich may result from hypoglycemiaor sepsis also leads to decreasedperistalsis in the left colonDecreased motility results in increasedabsorption of water from thecolon which eventuates in the formationof abnormal meconiumInfants with small left colon syndromepresent with progressive abdominaldistention vomiting and failureto pass meconium. Davis WS Campbell JB.
Meconium plug syndrome refers to a functional colonic obstruction in a newborn due to an obstructing meconium plug. Infants with small left colon syndrome present with progressive abdominal distention vomiting and failure to pass meconium. It is usually transient and affects the left colon with meconium plugging the bowel distal to this segment.
Neonatal small left colon syndrome is rare but an important differential in this situation and radiological findings are diagnostic. No reported cases within the same family could be found in the literature excepting 2 sets of twins.
Small left colon sydrome is subset of meconium plug syndrome in which an enema demonstrates an apparent transition zone between the dilated and the normal-to.
Infants with small left colon syndrome present with progressive abdominal distention vomiting and failure to pass meconium. Meconium plug syndrome usually occurs in infants who are otherwise healthy. Neonatal small left colon syndrome is a rare cause of bowel obstruction. Neonatal small left colon syndrome NSLCS should be considered as differential for neonatal intestinal obstruction especially with a background of maternal diabetes mellitus. Neonatal small left colon syndrome is rare but an important differential in this situation and radiological findings are diagnostic. Small left colon syndrome refers to a dysfunctional diminutive left colon that causes transient obstructive symptoms. Occurrence in asymptomatic infants of diabetic mothers. It is usually transient and affects the left colon with meconium plugging the bowel distal to this segment. Meconium plug syndrome refers to a functional colonic obstruction in a newborn due to an obstructing meconium plug.
Neonatal small left colon syndrome is rare but an important differential in this situation and radiological findings are diagnostic. Neonatal small left colon syndrome is rare but an important differential in this situation and radiological findings are diagnostic. Its etiology remains unknown but a significant association has been noted between maternal diabetes and small left colon. Meconium plug syndrome small left colon syndrome long segment Hirschsprung disease The rectosigmoid ratio was greater than 1 favoring meconium plug syndrome. Infants with small left colon syndrome present with progressive abdominal distention vomiting and failure to pass meconium. MATERIAL AND METHOD Nineteen infants presented inthe first to third days oflife each ofwhom had essen-tially the same clinical history suggesting low colonic obstruction. Plain abdominal radiographs show dilated intestinal loops.





























Post a Comment for "Small Left Colon Syndrome"