Parkinson Disease Differential Diagnosis
Parkinson disease differential diagnosis. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra a region of the midbrain leading to a dopamine deficit. Most parkinsonian patients present with clinical clues to guide the neurologists diagnostic assessment. It is a movement disorder presenting primarily with a combination of bradykinesia rigidity and tremor.
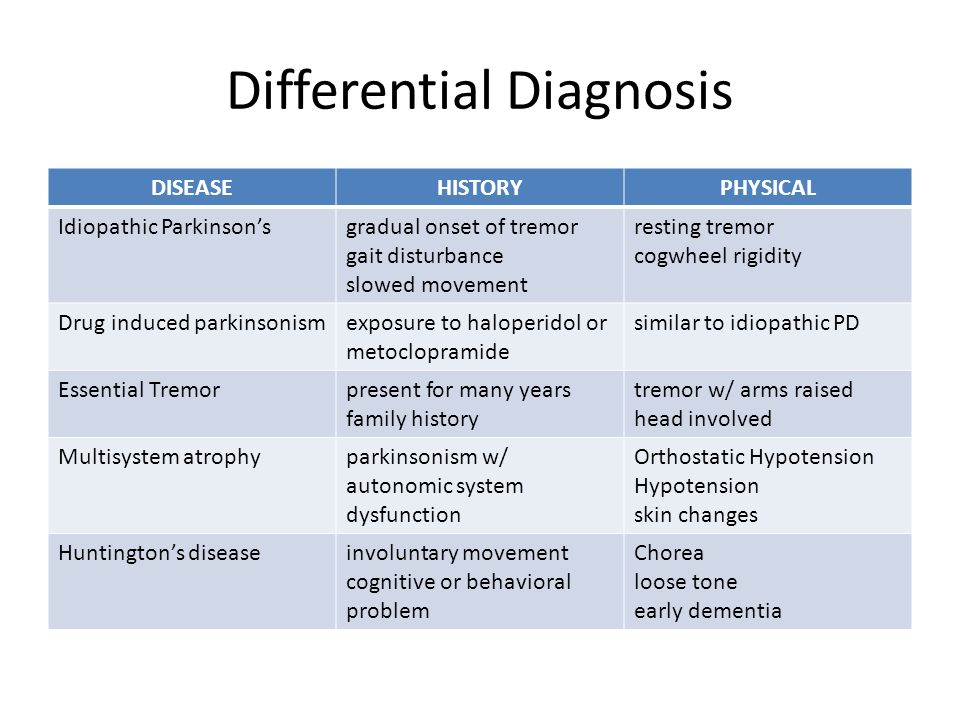
Drug-induced parkinsonism note. There is often no rigidity or resting tremor and there may be an action tremor. Those with Parkinsons can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems.
Most commonly the patient presents with a unilateral resting tremor bradykinesia and rigidity and frequently nonmotor symptoms as well. The most common form of parkinsonism is Parkinson disease PD a chronic progressive disorder caused by degenerative loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain and characterized clinically by asymmetric parkinsonism. Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized pathologically by loss of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra and by the presence of Lewy bodies.
The most important clues to the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease include of course elements of Parkinsonism usually 2 of 3 of the cardinal featuresbradykinesia tremor cogwheel rigidity. The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease PD is a common progressive neurodegenerative disease. Over recent decades improvements in the characterisation of the parkinsonian syndromes.
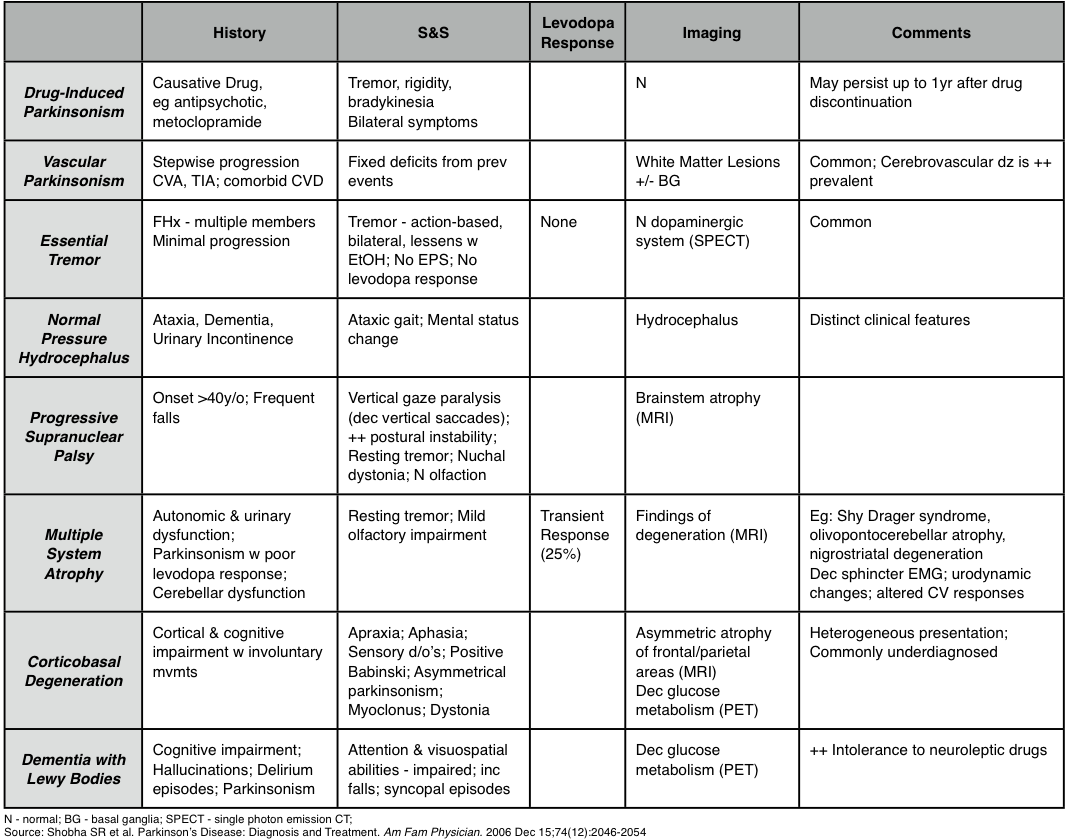
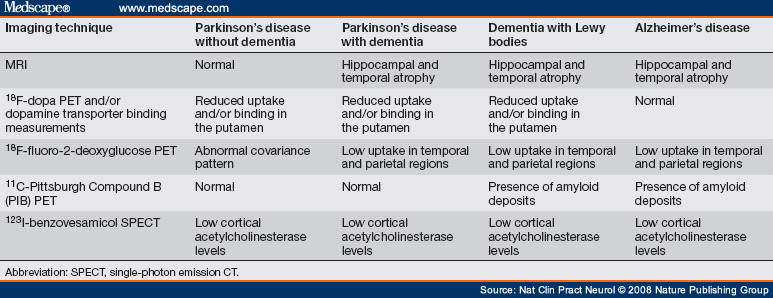
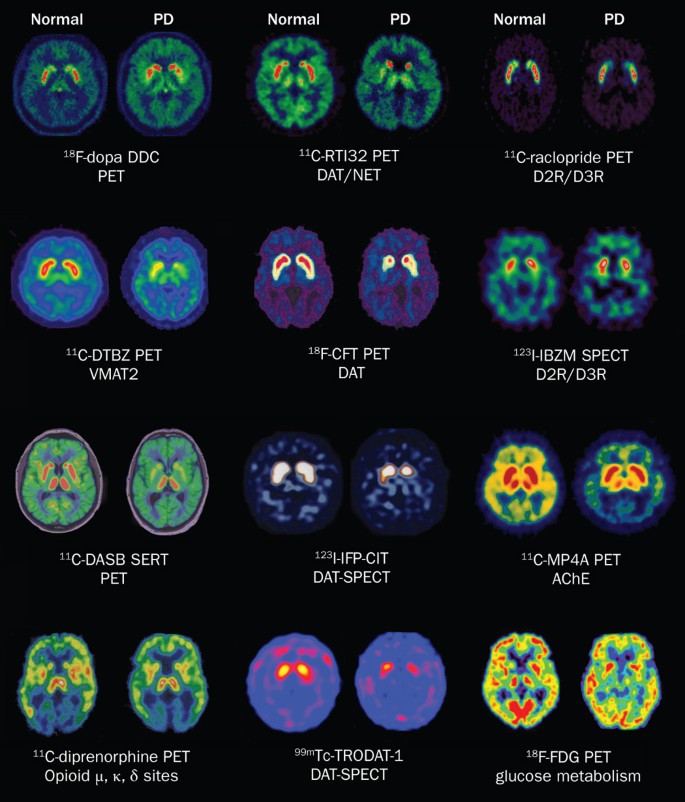
It typically presents with motor symptoms that are rapid in onset and bilateral. The diagnosis of Parkinsons disease and atypical parkinsonism is essentially based on clinical findings although imaging studies are important for making the differential diagnosis and for identifying structural lesions such as vascular lesions and tumors. 112 The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease display small and cramped handwriting which becomes progressively smaller micrographia with a tendency of the sentence to fall off the line.
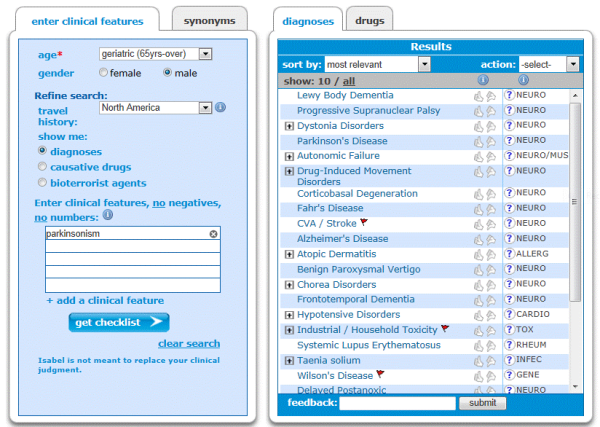
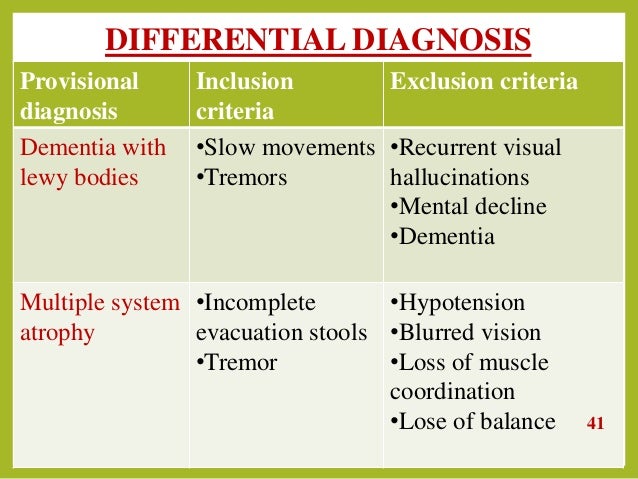
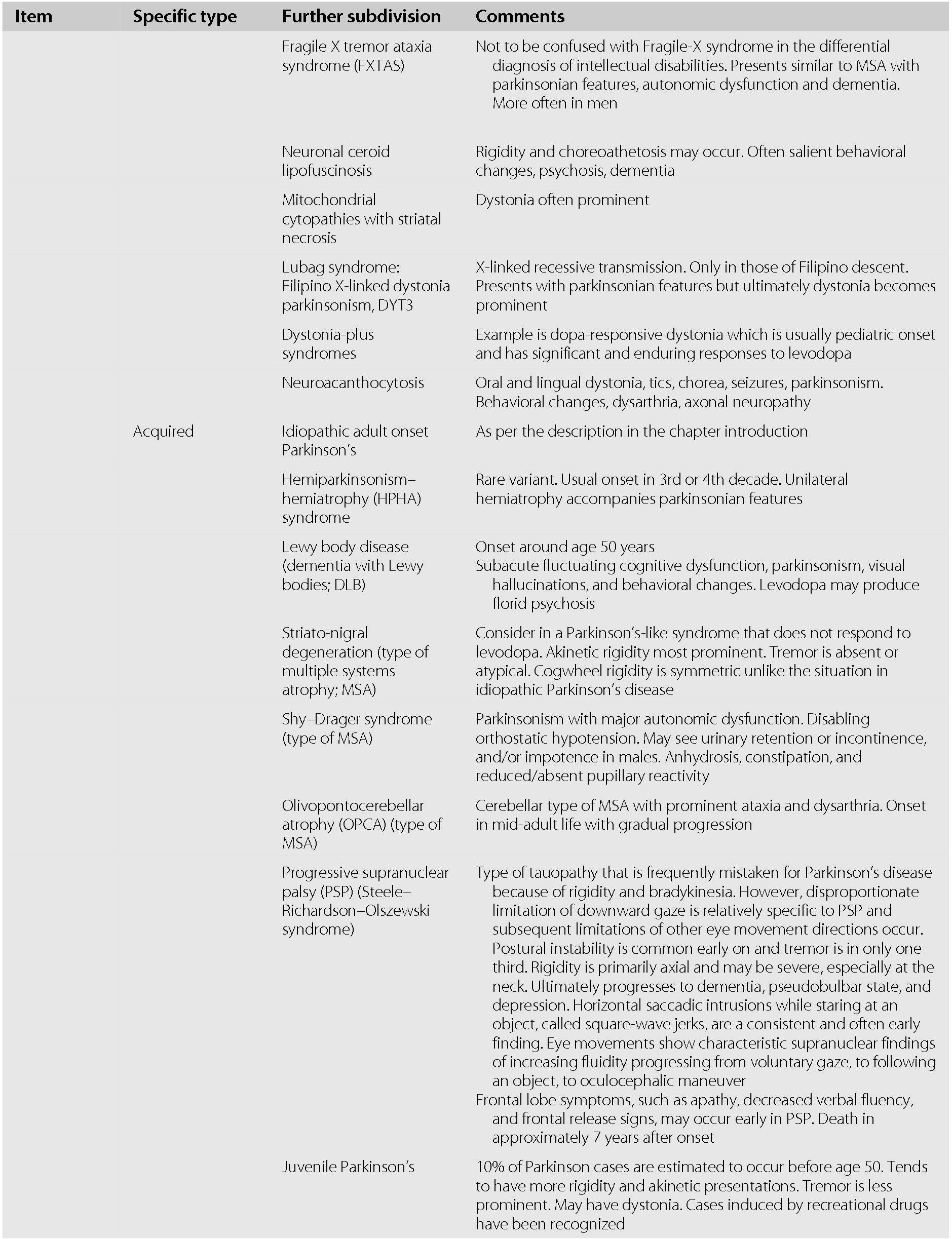
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosi s of Parkinson s Disease 5 Urinary dysfunction is especially debilitating for the patient and usually manifests as overactive bladder syndrome which has been attributed to the degeneration of central serotonergic projections. Diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons disease and a lacking improvement of motor symptoms suggests the presence of an atypical parkinso nian syndrome such as PSP MSA or CBD. The accurate diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons disease IPD is not only important for deciding on treatment strategies and providing a prognosis but also crucial for studies designed to investigate the aetiology and pathogenesis of parkinsonian disorders.
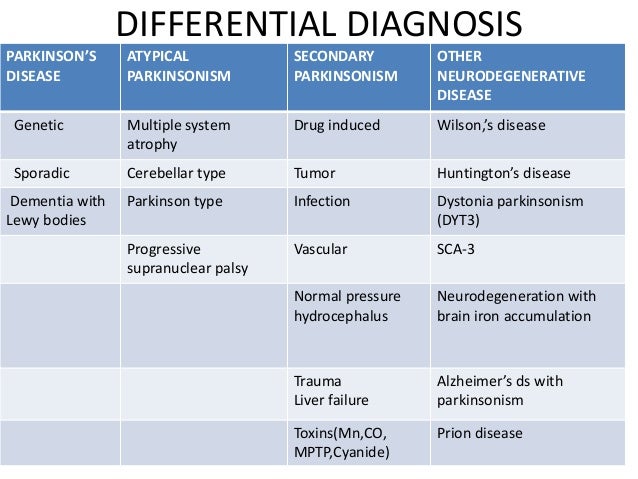
Parkinson disease PD is one of the most common neurologic disorders affecting approximately 1 of individuals older than 60 years and causing. The differential diagnosis of Parkinsons disease PD is vast encompassing a variety of neurodegenerative and metabolic conditions toxin exposures and vascular disease.
It is often not possible to distinguish between Parkinsons disease and drug-induced parkinsonism on the basis of clinical symptoms and signs alone.
Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is the most com-mon identifiable syndrome that can be diagnosed in the context of Parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism note. Parkinsons disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. On occasion the true bradykinesia of PD can be mistaken because the patient. The differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes is considered one of the most challenging in neurology and error rates in the clinical diagnosis can be high even at specialized centres. 112 The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease display small and cramped handwriting which becomes progressively smaller micrographia with a tendency of the sentence to fall off the line. Parkinsons disease PD diagnosis is yet largely based on the related clinical aspects. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra a region of the midbrain leading to a dopamine deficit. The accurate diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons disease IPD is not only important for deciding on treatment strategies and providing a prognosis but also crucial for studies designed to investigate the aetiology and pathogenesis of parkinsonian disorders.
It typically presents with motor symptoms that are rapid in onset and bilateral. There is often no rigidity or resting tremor and there may be an action tremor. The accurate diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons disease IPD is not only important for deciding on treatment strategies and providing a prognosis but also crucial for studies designed to investigate the aetiology and pathogenesis of parkinsonian disorders. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra a region of the midbrain leading to a dopamine deficit. Those with Parkinsons can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. Parkinsons disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosi s of Parkinson s Disease 5 Urinary dysfunction is especially debilitating for the patient and usually manifests as overactive bladder syndrome which has been attributed to the degeneration of central serotonergic projections.




































Post a Comment for "Parkinson Disease Differential Diagnosis"