Infection In Sickle Cell Disease
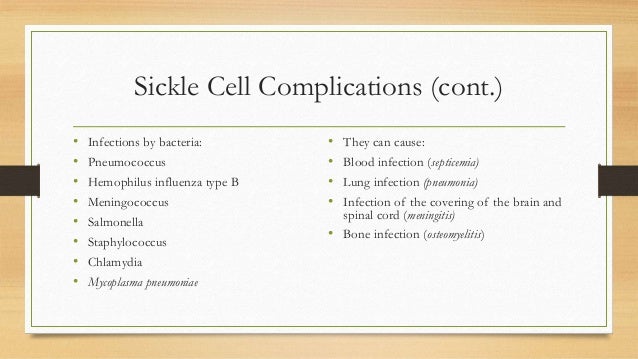
Infection in sickle cell disease. Bacterial infections afflicting these patients include fulminant meningitis and septicaemia caused by Str. Influenzae type b and non-typhoid salmonellosis. Sickle-cell disease SCD is one of the most common monogenic disorders worldwide characterized by wide variation in the associated diseases clinical manifestations and severity.
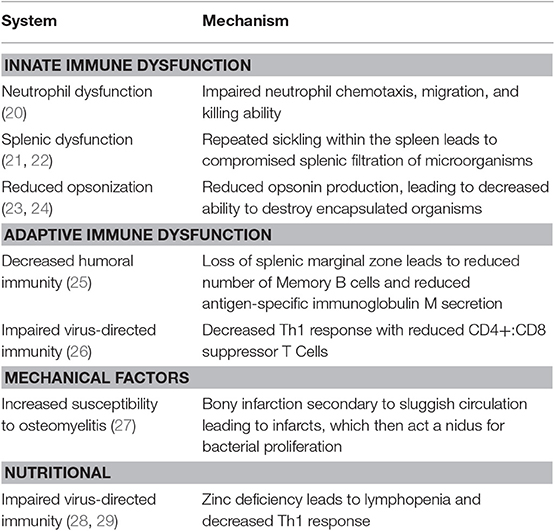
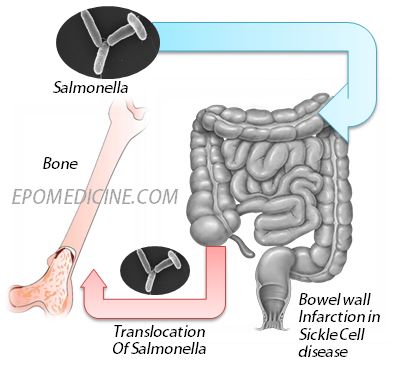
And Plasmodium falciparum in malarious areas are an important cause of morbidity and death in patients with sickle cell disease. In addition to their role in the initiation of the acute pa. Bacterial infection is frequent in patients with sickle cell disease.
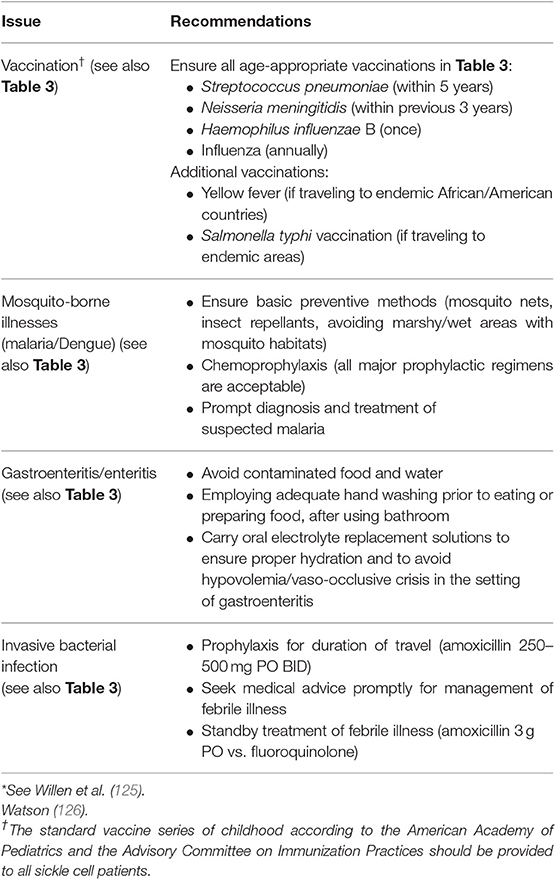
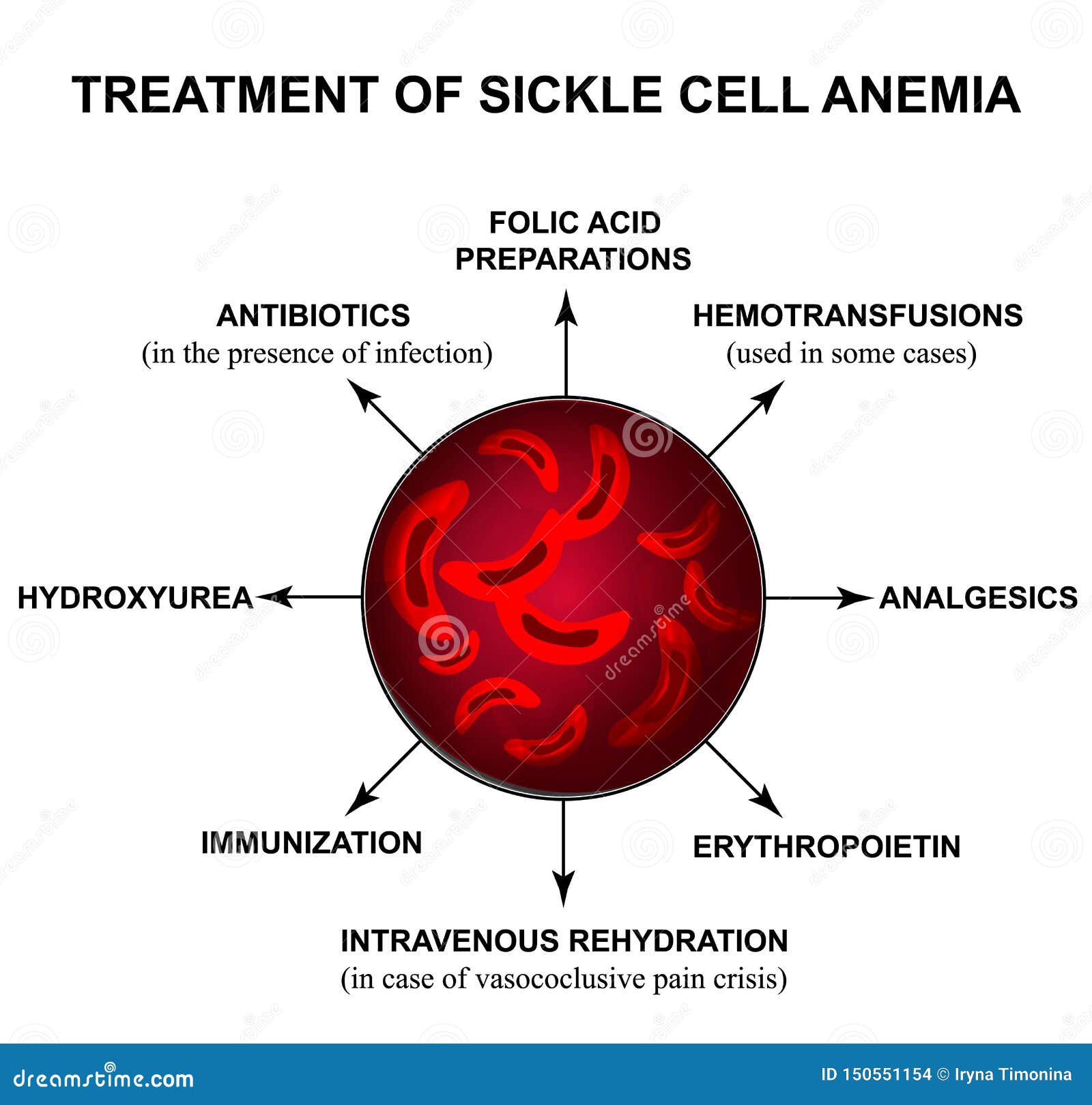
They include pneumonia blood stream infections meningitis and bone infections. Prevention is directed against pneumococcal disease and includes both vaccination and prophylactic antibiotics. In people with sickle cell disease the spleen does not work correctly.
Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders that affects hemoglobin the protein that carries oxygen through the body. The sickle gene confers an increased susceptibility to infection especially to certain bacterial pathogens and at the same time infection provokes a cascade of SCD-specific pathophysiological changes. Sickle cell disease SCD is commonly encountered in Africa and Middle Eastern countries.
Long-term pain may develop as people get older. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. 6 The disease is characterized by vaso-occlusion of blood vessels by abnormal red blood cells white blood cells and platelets resulting in.
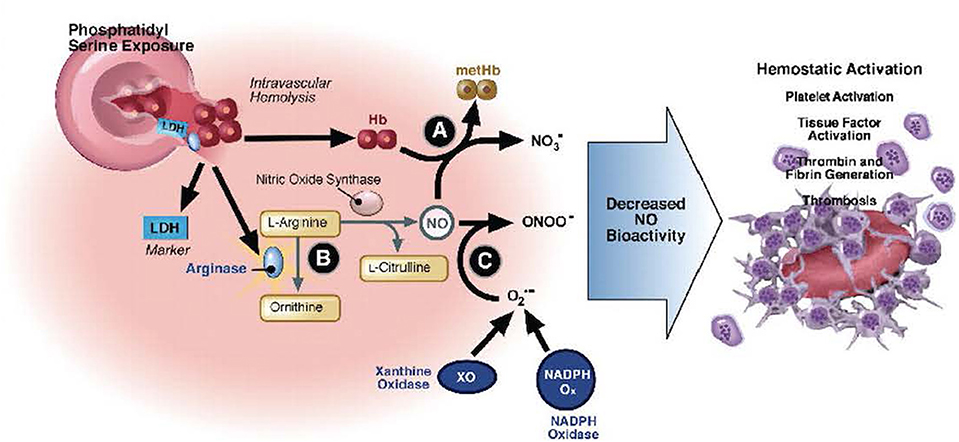
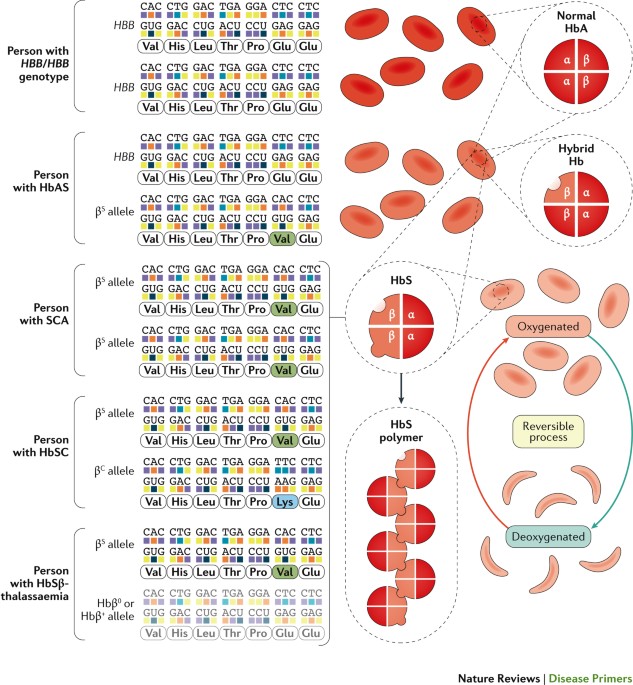
The primary β-globin gene mutation that causes sickle cell disease SCD has significant pathophysiological consequences that result in hemolytic events and the induction of the inflammatory processes that ultimately lead to vaso-occlusion. Hemoglobin SS HBSS genotype is associated with most of these complications. Streptococos pneumoniae Salmonella spp Hib Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp.
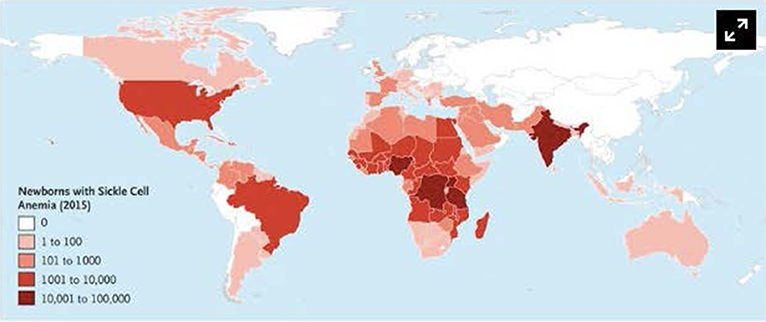
Children with sickle cell disease SCD are at increased risk for invasive infection with encapsulated bacteria. Sickle cell disease SCD is an inherited disorder of hemoglobin that predominantly involves individuals of African descent affecting 100 000 individuals in the United States and millions in sub-Saharan Africa the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent.
Infarction is a debilitating and significant complication of sickle cell disease and it may occur anywhere in the skeleton.
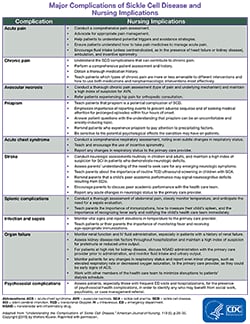
Infection - People with sickle cell disease are at high risk of life-threatening blood infections so with any fever temperature 101F or higher or sign of serious infection emergency medical care. They include pneumonia blood stream infections meningitis and bone infections. And Plasmodium falciparum in malarious areas are an important cause of morbidity and death in patients with sickle cell disease. Historically infection is a major cause of. People with sickle cell disease have an increased risk of developing certain infections. Infection is a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality in sickle cell disease SCD. As HbS replaces HbF in the early months of life problems associated with sickling and red cell membrane damage begin. The primary β-globin gene mutation that causes sickle cell disease SCD has significant pathophysiological consequences that result in hemolytic events and the induction of the inflammatory processes that ultimately lead to vaso-occlusion. The resulting rigid cells.
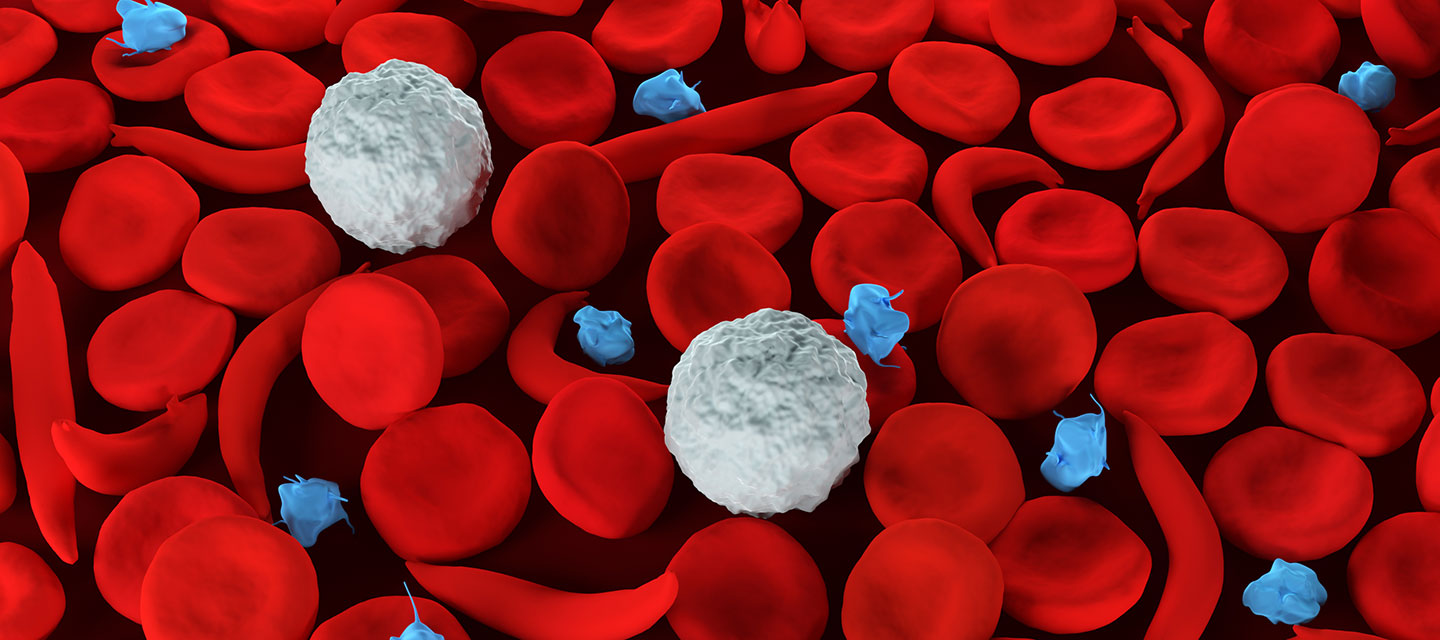
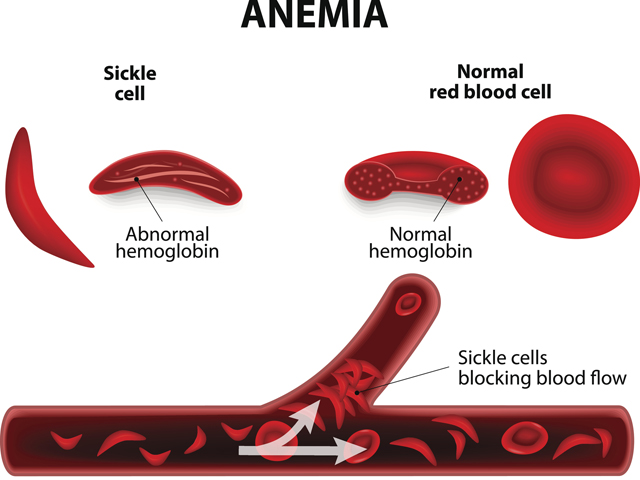
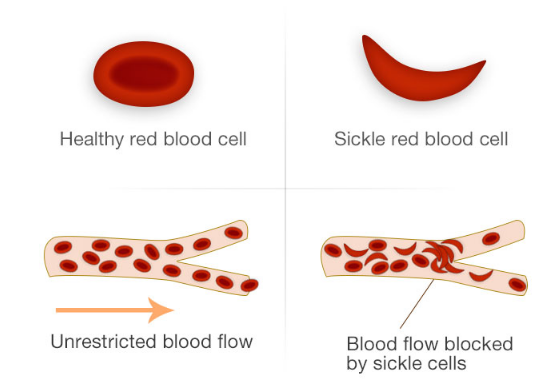
Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders that affects hemoglobin the protein that carries oxygen through the body. Bacterial infection is frequent in patients with sickle cell disease. Life-threatening acute physiologic crises may occur on a background of progressive diminishing vital organ function. The primary β-globin gene mutation that causes sickle cell disease SCD has significant pathophysiological consequences that result in hemolytic events and the induction of the inflammatory processes that ultimately lead to vaso-occlusion. It results directly from the sickling of red blood cells in the bone marrow which causes stasis of blood and sequestration of cells. Streptococos pneumoniae Salmonella spp Hib Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. Normally red blood cells are disc shaped and flexible to move easily through the blood vessels.



































Post a Comment for "Infection In Sickle Cell Disease"